
如何構(gòu)建一個Linux Shell(三)
這是有關(guān)如何構(gòu)建Linux Shell的教程的第三部分。在本教程的上半部分,我們實現(xiàn)了詞法掃描器。現(xiàn)在,讓我們將目光轉(zhuǎn)向解析器。回顧一下,解析器是命令行解釋器的一部分,它調(diào)用詞法掃描器以檢索令牌,然后從這些令牌中構(gòu)造一個抽象語法樹或AST。這個AST是我們將傳遞給執(zhí)行者的東西,好吧,被執(zhí)行。

解析簡單命令
我們的解析器將僅包含一個函數(shù), parse_simple_command()。在本教程的后續(xù)部分中,我們將添加更多功能以使我們的Shell能夠解析循環(huán)和條件表達(dá)式。
因此,讓我們開始對解析器進行編碼。您可以先創(chuàng)建一個名為parser.h 在源目錄中,您將在其中添加以下代碼:
#ifndef PARSER_H
#define PARSER_H
#include "scanner.h" /* struct token_s */
#include "source.h" /* struct source_s */
struct node_s *parse_simple_command(struct token_s *tok);
#endif
沒什么,只是聲明我們唯一的解析器功能。
接下來,建立 parser.c 并添加以下代碼:
#include
#include "shell.h"
#include "parser.h"
#include "scanner.h"
#include "node.h"
#include "source.h"
struct node_s *parse_simple_command(struct token_s *tok)
{
if(!tok)
{
return NULL;
}
struct node_s *cmd = new_node(NODE_COMMAND);
if(!cmd)
{
free_token(tok);
return NULL;
}
struct source_s *src = tok->src;
do
{
if(tok->text[0] == ' ')
{
free_token(tok);
break;
}
struct node_s *word = new_node(NODE_VAR);
if(!word)
{
free_node_tree(cmd);
free_token(tok);
return NULL;
}
set_node_val_str(word, tok->text);
add_child_node(cmd, word);
free_token(tok);
} while((tok = tokenize(src)) != &eof_token);
return cmd;
}
很簡單,對吧?要解析一個簡單的命令,我們只需要調(diào)用tokenize() 檢索輸入令牌,一個接一個,直到我們得到一個換行符(我們在以下行中對其進行測試: if(tok->text[0] == ' ')),或者我們到達(dá)輸入的結(jié)尾(我們知道當(dāng)我們收到 eof_token令牌。請參閱上一清單底部附近的循環(huán)條件表達(dá)式。我們使用輸入令牌來創(chuàng)建AST,它是一個樹狀結(jié)構(gòu),其中包含有關(guān)命令組件的信息。詳細(xì)信息應(yīng)足以使執(zhí)行程序正確執(zhí)行命令。例如,下圖顯示了簡單命令的AST外觀。
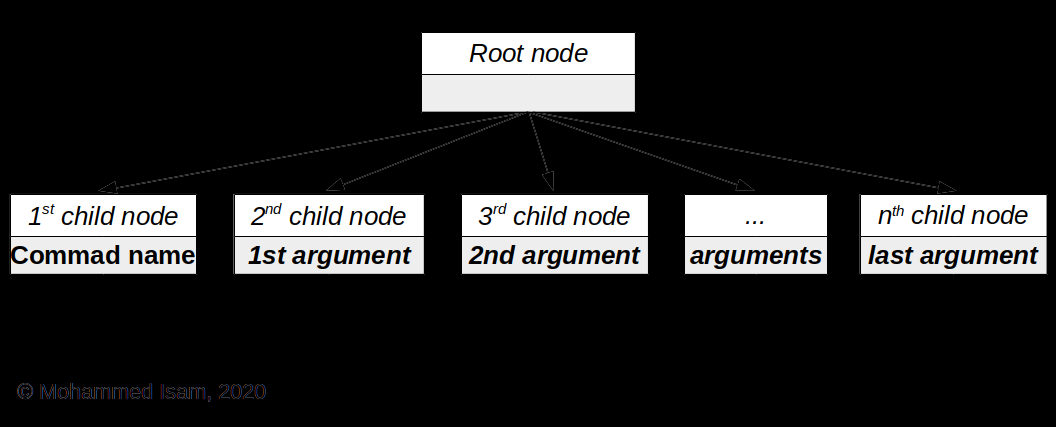
命令的AST中的每個節(jié)點都必須包含有關(guān)其表示的輸入令牌的信息(例如原始令牌的文本)。該節(jié)點還必須包含指向其子節(jié)點(如果該節(jié)點是根節(jié)點)及其兄弟節(jié)點(如果該節(jié)點是子節(jié)點)的指針。因此,我們需要定義另一個結(jié)構(gòu),struct node_s,我們將用它來表示AST中的節(jié)點。
繼續(xù)創(chuàng)建一個新文件, node.h,并向其中添加以下代碼:
#ifndef NODE_H
#define NODE_H
enum node_type_e
{
NODE_COMMAND, /* simple command */
NODE_VAR, /* variable name (or simply, a word) */
};
enum val_type_e
{
VAL_SINT = 1, /* signed int */
VAL_UINT, /* unsigned int */
VAL_SLLONG, /* signed long long */
VAL_ULLONG, /* unsigned long long */
VAL_FLOAT, /* floating point */
VAL_LDOUBLE, /* long double */
VAL_CHR, /* char */
VAL_STR, /* str (char pointer) */
};
union symval_u
{
long sint;
unsigned long uint;
long long sllong;
unsigned long long ullong;
double sfloat;
long double ldouble;
char chr;
char *str;
};
struct node_s
{
enum node_type_e type; /* type of this node */
enum val_type_e val_type; /* type of this node's val field */
union symval_u val; /* value of this node */
int children; /* number of child nodes */
struct node_s *first_child; /* first child node */
struct node_s *next_sibling, *prev_sibling; /*
* if this is a child node, keep
* pointers to prev/next siblings
*/
};
struct node_s *new_node(enum node_type_e type);
void add_child_node(struct node_s *parent, struct node_s *child);
void free_node_tree(struct node_s *node);
void set_node_val_str(struct node_s *node, char *val);
#endif
的 node_type_e枚舉定義了我們的AST節(jié)點的類型。目前,我們只需要兩種類型。第一種類型表示簡單命令的AST的根節(jié)點,而第二種類型表示簡單命令的子節(jié)點(包含命令名稱和參數(shù))。在本教程的下一部分中,我們將向該枚舉添加更多節(jié)點類型。
的 val_type_e枚舉表示我們可以存儲在給定節(jié)點結(jié)構(gòu)中的值的類型。對于簡單的命令,我們僅使用字符串(VAL_STR枚舉類型)。在本系列的稍后部分,我們將在處理其他類型的復(fù)雜命令時使用其他類型。
的 symval_uunion表示我們可以存儲在給定節(jié)點結(jié)構(gòu)中的值。每個節(jié)點只能具有一種類型的值,例如字符串或數(shù)字值。我們通過引用適當(dāng)?shù)穆?lián)合成員來訪問節(jié)點的值(sint 對于帶符號的長整數(shù), str 用于字符串等)。
的 struct node_s結(jié)構(gòu)代表AST節(jié)點。它包含一些字段,這些字段告訴我們有關(guān)節(jié)點類型,節(jié)點值的類型以及值本身的信息。如果這是根節(jié)點,則children 字段包含子節(jié)點的數(shù)量,并且 first_child 指向第一個子節(jié)點(否則它將是 NULL)。如果這是一個子節(jié)點,我們可以按照以下步驟遍歷AST節(jié)點:next_sibling 和 prev_sibling 指針。
如果要檢索節(jié)點的值,則需要檢查 val_type 字段,然后根據(jù)我們在其中找到的內(nèi)容,訪問 val領(lǐng)域。對于簡單命令,所有節(jié)點都將具有以下屬性:
.type => NODE_COMMAND (根節(jié)點)或 NODE_VAR (命令名稱和參數(shù)列表)
.val_type => VAL_STR
.val.str =>指向字符串值的指針
現(xiàn)在讓我們編寫一些函數(shù)來幫助我們處理節(jié)點結(jié)構(gòu)。
創(chuàng)建一個名為 node.c 并添加以下代碼:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "shell.h"
#include "node.h"
#include "parser.h"
struct node_s *new_node(enum node_type_e type)
{
struct node_s *node = malloc(sizeof(struct node_s));
if(!node)
{
return NULL;
}
memset(node, 0, sizeof(struct node_s));
node->type = type;
return node;
}
void add_child_node(struct node_s *parent, struct node_s *child)
{
if(!parent || !child)
{
return;
}
if(!parent->first_child)
{
parent->first_child = child;
}
else
{
struct node_s *sibling = parent->first_child;
while(sibling->next_sibling)
{
sibling = sibling->next_sibling;
}
sibling->next_sibling = child;
child->prev_sibling = sibling;
}
parent->children++;
}
void set_node_val_str(struct node_s *node, char *val)
{
node->val_type = VAL_STR;
if(!val)
{
node->val.str = NULL;
}
else
{
char *val2 = malloc(strlen(val)+1);
if(!val2)
{
node->val.str = NULL;
}
else
{
strcpy(val2, val);
node->val.str = val2;
}
}
}
void free_node_tree(struct node_s *node)
{
if(!node)
{
return;
}
struct node_s *child = node->first_child;
while(child)
{
struct node_s *next = child->next_sibling;
free_node_tree(child);
child = next;
}
if(node->val_type == VAL_STR)
{
if(node->val.str)
{
free(node->val.str);
}
}
free(node);
}
的 new_node() 函數(shù)創(chuàng)建一個新節(jié)點并將其設(shè)置為 type 領(lǐng)域。
的 add_child_node() 函數(shù)通過添加新的子節(jié)點并增加根節(jié)點的擴展來擴展簡單命令的AST children領(lǐng)域。如果根節(jié)點沒有子節(jié)點,則將新的子節(jié)點分配給first_child根節(jié)點的字段。否則,該孩子將被添加到孩子列表的末尾。
的 set_node_val_str()函數(shù)將節(jié)點的值設(shè)置為給定的字符串。它將字符串復(fù)制到新分配的內(nèi)存空間,然后設(shè)置val_type 和 val.str字段。將來,我們將定義類似的函數(shù),以使我們可以將節(jié)點值設(shè)置為不同的數(shù)據(jù)類型,例如整數(shù)和浮點數(shù)。
的 free_node_tree()函數(shù)釋放節(jié)點結(jié)構(gòu)使用的內(nèi)存。如果節(jié)點有子節(jié)點,則以遞歸方式調(diào)用該函數(shù)以釋放每個子節(jié)點。
解析器就這些了。現(xiàn)在讓我們編寫命令執(zhí)行器。
執(zhí)行簡單命令
與解析器類似,執(zhí)行程序?qū)H包含一個函數(shù), do_simple_command()。在本教程的后續(xù)部分中,我們將添加更多功能以使我們能夠執(zhí)行各種命令,例如循環(huán)和條件表達(dá)式。
創(chuàng)建一個名為 executor.h,并添加以下代碼:
#ifndef BACKEND_H
#define BACKEND_H
#include "node.h"
char *search_path(char *file);
int do_exec_cmd(int argc, char **argv);
int do_simple_command(struct node_s *node);
#endif
只是一些功能原型。現(xiàn)在創(chuàng)建executor.c 并定義以下功能:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "shell.h"
#include "node.h"
#include "executor.h"
char *search_path(char *file)
{
char *PATH = getenv("PATH");
char *p = PATH;
char *p2;
while(p && *p)
{
p2 = p;
while(*p2 && *p2 != ':')
{
p2++;
}
int plen = p2-p;
if(!plen)
{
plen = 1;
}
int alen = strlen(file);
char path[plen+1+alen+1];
strncpy(path, p, p2-p);
path[p2-p] = ' 主站蜘蛛池模板: 动漫www.被爆羞羞av44 | 久久久成人动漫 | 私人vps一夜爽毛片免费 | 色99导航 | 久久精品动漫 | 爆乳美女脱内衣18禁裸露网站 | 黄色片大全网 | 中文字幕日韩精品有码视频 | 精品国产成人网站一区二区 | 亚洲制服丝袜欧美 | 人妻少妇无码精品视频区 | 免费无遮挡禁18污污网站 | 婷婷中文 | 夂久亚州精华国产精华华液 | 精品久久久久久一区二区里番 | 国产精品爱啪在线线免费观看 | 99热亚洲 | 东京一本到熟无码免费视频 | 日本的黄色一级片 | 99国产揄拍国产精品人妻 | 成人欧美一区二区三区黑人免费 | 性高湖久久久久久久久3小时 | 男女裸体下面进入的免费视频 | 依依成人精品视频在线观看 | 亚洲精品久久久久77777 | av大片网址 | 国产成人亚洲日韩欧美久久久 | 天海翼四虎精品正在播放 | 日韩欧美人妻一区二区三区 | 亚洲精品国产乱码在线看蜜月 | 亚洲欧洲日产国码AV天堂偷窥 | 亚洲国产av玩弄放荡人妇 | 九九热色 | 辽宁人妻Chinese | 国产一区二区免费在线播放 | 麻豆精品三区 | 欧美成人精品在线 | 日本小视频网址 | 四虎影视免费永久在线 | 成人免费看的A级毛片 | 少妇无码太爽了在线播放 |


 400-626-7377
400-626-7377